

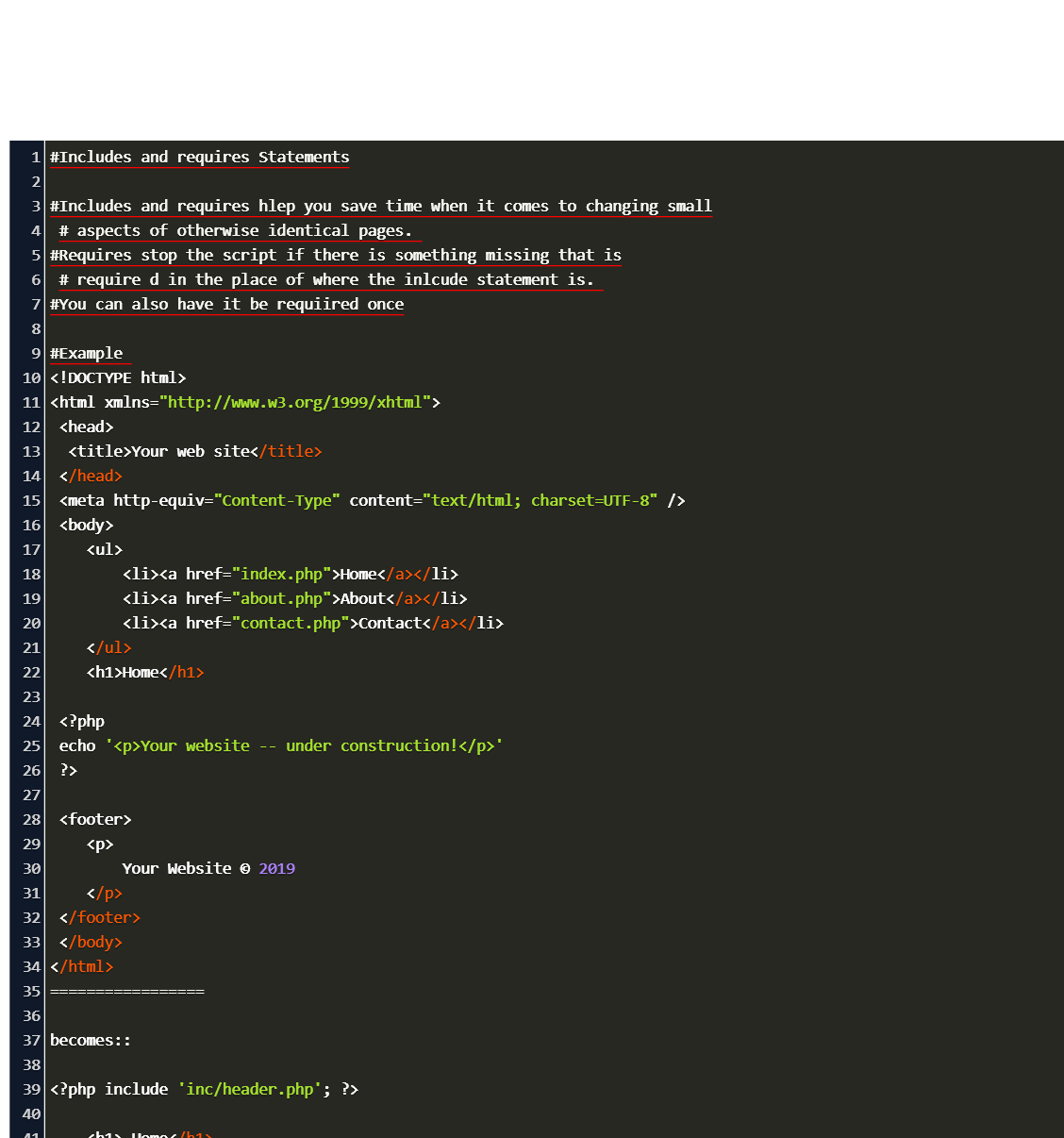
As you may suspect, of these four statements only the include and require statements actually differ with any great significance, and it is those differences that I'll focus on. Regardless of the reasons, inclusion of external files is accomplished through the include, include_once, require, and require_once PHP statements. Furthermore, by storing sensitive static information such as database login information in separate files, they can be safely placed outside the Web tree of the server and thus be inaccessible by the public.

In PHP, this organization is accomplished by separating your scripts into multiple files and including them when appropriate. In this respect, and as you accumulate an ever-growing library of functions, the need to organize them becomes more and more paramount. So lines after the first "0A" are totally different.Įg.It is always good practice to make your scripts as modular as possible, designing your functions in such a way that they can be used in other PHP scripts. Moreover, file() causes a serious problem in UTF-16LE.įile() loses first "0A" (the first half of "0A00")!Īnd the next line begins with "00" (the rest of "0A00"). The former may miss the last line of the string.)įile() seems to have a problem in handlingįile() is likely to think "\n"=LF (0A) as a line-ending. ("file()'s problem with UTF-16" is wrong. PS: also see: to read CSV data into an array (4) = with or without 1st row = head (true/false) (3) = values enclosed by (e.g: ' or " or ^ or. (1) = the file with CSV data (url / string) (see 4th parameter of function call as true / false)

Read from CSV data (file) into an array with named keys
Php include file archive#
Getting Started Introduction A simple tutorial Language Reference Basic syntax Types Variables Constants Expressions Operators Control Structures Functions Classes and Objects Namespaces Enumerations Errors Exceptions Fibers Generators Attributes References Explained Predefined Variables Predefined Exceptions Predefined Interfaces and Classes Predefined Attributes Context options and parameters Supported Protocols and Wrappers Security Introduction General considerations Installed as CGI binary Installed as an Apache module Session Security Filesystem Security Database Security Error Reporting User Submitted Data Hiding PHP Keeping Current Features HTTP authentication with PHP Cookies Sessions Dealing with XForms Handling file uploads Using remote files Connection handling Persistent Database Connections Command line usage Garbage Collection DTrace Dynamic Tracing Function Reference Affecting PHP's Behaviour Audio Formats Manipulation Authentication Services Command Line Specific Extensions Compression and Archive Extensions Cryptography Extensions Database Extensions Date and Time Related Extensions File System Related Extensions Human Language and Character Encoding Support Image Processing and Generation Mail Related Extensions Mathematical Extensions Non-Text MIME Output Process Control Extensions Other Basic Extensions Other Services Search Engine Extensions Server Specific Extensions Session Extensions Text Processing Variable and Type Related Extensions Web Services Windows Only Extensions XML Manipulation GUI Extensions Keyboard Shortcuts ? This help j Next menu item k Previous menu item g p Previous man page g n Next man page G Scroll to bottom g g Scroll to top g h Goto homepage g s Goto search


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
